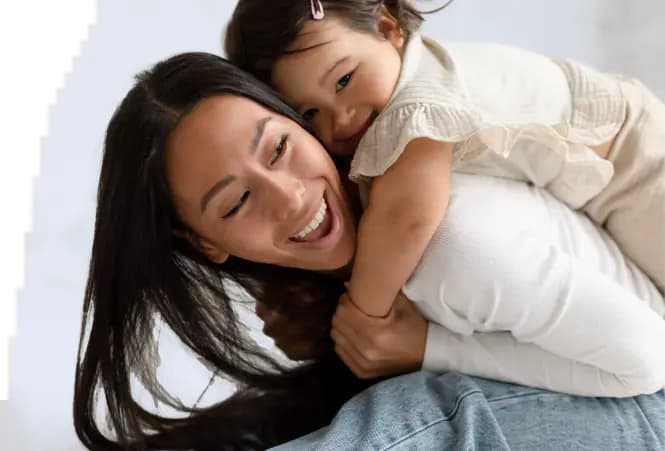
Eating well-balanced meals is important at all times, but it is even more essential when you are pregnant to fulfil the needs of your developing baby. The key is to start small and be consistent. You need to change your eating and drinking habits and consume more nutritious foods and drinks to meet the extra demands of pregnancy. There’s no bigger motherhood minefield than deciding what not to eat when you’re pregnant - but it’s often hard to distinguish between fact and fiction and figure out whether we’re being sensible or overcautious. Foods You Shouldn’t Eat While Pregnant:
MEAT

Raw Meat: Any raw meat, raw chicken or other poultry, uncooked seafood, raw cured meat, such as parma ham, chorizo, pepperoni and salami, under-cooked meat etc. should be avoided during pregnancy because of the risk of contamination with coliform bacteria, toxoplasma, and salmonella. Avoid undercooked meat, especially sausages or minced meat. Be careful to cook them thoroughly so there’s no trace of pink or blood. Processed Meats: Ham, salami, bologna, chicken, meat etc. must be avoided. Cold chicken or turkey, e.g. used in sandwich bars is not recommended.
Cooked meats must be cooked thoroughly and consumed while hot. Stuffing from chicken or poultry must be avoided unless cooked separately and must be consumed while hot. Deli meat should be avoided during pregnancy as these have been known to be contaminated with listeria, causing miscarriage. Listeria has the ability to cross the placenta and may infect the baby, which could lead to infection or blood poisoning and may be life-threatening. If you are pregnant and you are considering eating deli meats, make certain that you reheat the meat until it is steaming.
SEA FOOD

Fish with Mercury: Fish that contain high levels of mercury has been linked to developmental delays and brain damage, for example - shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tile fish. Canned, chunk light tuna generally has a lower amount of mercury than other tuna, but still should only be eaten in moderation. Sushi: Certain types of fish used in sushi should also be avoided due to high levels of mercury. Sushi should be avoided during pregnancy. Store-bought: Don’t eat store bought packed meals. Avoid raw seafood. Avoid ready-to-eat chilled peeled prawns. Cooked fish and seafood: Cook thoroughly until steaming and eat while hot. Store leftovers in the fridge to reheat and use within a day of cooking. No more than one serving (100g cooked) of shark/flake, marlin or broadbill /swordfish per fortnight. Smoked Seafood: Refrigerated, smoked seafood often labeled as lox, nova style, kippered, or jerky should be avoided because it could be contaminated with listeria. (These are safe to eat when they are in an ingredient in a meal that has been cooked, like a casserole.)
Contaminated fish: Eating contaminated fish should be avoided during pregnancy as these are fish exposed to industrial pollutants from contaminated lakes and rivers to high levels of poly chlorinated biphenyls like bluefish, striped bass, salmon, pike, trout, and walleye. Raw Shellfish: The majority of seafood-borne illness is caused by undercooked shellfish, which include oysters, clams, and mussels as they give you food poisoning. Cooking helps prevent some types of infection, but it does not prevent the algae-related infections that are associated with red tides. Raw shellfish pose a concern for everybody, and they should be avoided altogether during pregnancy. Oily fish: Limit oily fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, herring, pilchards) to no more than two portions a week as they contain pollutants.
EGGS

Raw Eggs: Raw eggs or any foods that contain raw eggs e.g. home-made mayonnaise, chocolate mousse, aioli, homemade ice cream or custards, Caesar dressings and hollandaise sauces should be avoided because of the potential exposure to salmonella. If the recipe is cooked at some point, this will reduce the exposure to salmonella. Commercially manufactured ice cream, dressings, and eggnog is made with pasteurized eggs and do not increase the risk of salmonella. In non-refrigerated commercial products e.g. mayonnaise and aioli, check ‘best before’ or ‘use-by’ date and follow storage instructions. Restaurants should be using pasteurized eggs in any recipe that is made with raw eggs. Cooked egg dishes like fried eggs, scrambled eggs, quiche etc. should be cooked thoroughly. Don’t use cracked or dirty eggs.
DAIRY

Unpasteurized (raw): Unpasteurized milk may contain listeria, toxoplasmosis, campylobacter, e coli or salmonella. Listeriosis can cause miscarriage, stillbirth or severe illness in newborns. Toxoplasmosis is also a risk with unpasteurized milk and milk products, which in rare cases can lead to abnormalities in the foetus. Pasteurized: Check ‘best before’ or ‘use-by’ date and follow storage instructions for milk, cream, yogurt etc. When you are pregnant, your immune system is lower and this is why unpasteurized milk should be avoided during pregnancy but is fine any other time. This also applies to goat's milk and sheep's milk.
CHEESE
Soft Cheeses: Soft cheeses are made with unpasteurized milk so should be avoided. Imported soft cheeses may contain listeria, salmonella, E COLI. You would need to avoid soft cheeses such as brie, Camembert, Roquefort, feta, ricotta, Gorgonzola, and Mexican style cheeses that include queso blanco and queso fresco, unless they clearly state that they are made from pasteurized milk. All soft non-imported cheeses made with pasteurized milk are safe to eat. Processed cheese, cheese spreads, cottage cheese, cream cheese etc.: Store in the fridge, eat within two days of opening pack. Hard cheese e.g. cheddar, tasty cheese: store in the fridge.
ICE-CREAM
Soft serve: avoid Fried ice-cream : avoid Packaged frozen ice-cream: Keep and eat frozen.
CUSTARD
Store-bought: Can be eaten cold if freshly opened. Store in fridge to reheat and use within a day of opening. Check best before or use-by date. Home-made: Cook thoroughly and eat while hot. Store in fridge. Always reheat and use within a day of making.
PATE
Eating pate should be avoided during pregnancy because they may contain the bacteria listeria. Liver pate can also have high levels of vitamin A, which is harmful to the baby. Refrigerated pate or meat spreads: should be avoided. Canned pate or shelf-safe meat spreads can be eaten.
CAFFEINE

Although most studies show that caffeine intake in moderation is permissible, there are others that show that caffeine intake may be related to miscarriages, premature birth, low birth weight, and withdrawal symptoms in infants. Avoid caffeine during the first trimester to reduce the likelihood of a miscarriage. As a general rule, caffeine should be limited to fewer than 200 mg per day during pregnancy. Caffeine is a diuretic, which means it helps eliminate fluids from the body. This can result in water and calcium loss. It is important that you drink plenty of water, juice, and milk rather than caffeinated beverages. Caffeine is found in tea and coffee, cola and other soft drinks and chocolate. You should limit your caffeine intake to no more than 200mg a day during your pregnancy. CAFFEINE TYPE AMOUNT OF CAFFEINE (mg/250mL)) A can of cola has around 30 – 40 mg of caffeine, a mug of tea has around 75mg, a bar of plain chocolate has around 50 mg (20mg per 20g bar), Hot Chocolate or Cocoa 50 – 70mg. A cup of instant coffee has around 100mg, a mug of filter coffee has around 140mg, Espresso Coffees (e.g. cappuccino, flat white) 100 - 200mg, Brewed/Plunger Coffee 100 - 500mg, Decaffeinated Coffee 2 - 4, and Energy Drinks 80mg.
ALCOHOL

There is no amount of alcohol that is known to be safe during pregnancy and breast feeding. Prenatal exposure to alcohol can interfere with the healthy development of the baby. Depending on the amount, timing, and pattern of use, alcohol consumption during pregnancy can lead to Fetal Alcohol Syndrome or other developmental disorders. If you consumed alcohol before you knew you were pregnant, stop drinking now. You should continue to avoid alcohol during breastfeeding.
VEGETABLE AND HERBS
Fresh vegetables and herb: Wash well just before eating raw or wash before cooking. Unwashed Vegetables: Unwashed vegetables should be avoided during pregnancy to avoid potential exposure to toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis may contaminate the soil where the vegetables were grown. Frozen vegetables. Cook, don’t eat uncooked. Bean Sprouts: Alfalfa sprouts, broccoli sprouts, onion sprouts, sunflower. Don’t eat raw or lightly cooked.
SALADS
Pre-prepared or pre-packaged salads including fruit salad like stuff from salad bars etc. must be avoided. Home-made: Wash salad ingredients well just before making and eating salads; store any leftover salads in fridge and use within a day of preparation.
FRUIT
Whole fresh fruits: Wash well before eating. Leftovers Cooked foods: Store leftovers covered in the fridge, eat within a day and always reheat until steaming hot. Canned Foods, tinned fruit, vegetables, fish etc.: Store unused portions in the fridge in clean, sealed containers and use within a day. Liver and other foods containing vitamin A: Avoid liver and liver products, such as liver pâté and liver sausage. It's not safe to take multivitamins containing vitamin A or fish liver oils, such as cod liver oil. Also steer clear of any foods that have vitamin A added (they may say 'fortified with vitamin A'). Liver has high levels of vitamin A, and too much of this can harm your baby. Apart from these, some common food items where people are generally confused: HUMMUS: Store-bought or home-made. Store in fridge, eat within two days of opening or making.
SOY: All soy products like tofu, soy milk, soy yogurt etc. - check ‘best before’ or ‘use-by’ date. Follow storage instructions. PAPAYA: There is little research that has been done in this area of the safely of papaya consumption in pregnancy and from what is out there, there may be a possible link to contractions with unripe papaya. With this said, as there needs to be further research done in this area it would probably be advisable to avoid papayas as the information is limited.
PARSLEY: It is not one of the foods to avoid in pregnancy. In fact it is a food rich in Vitamin C and K and a good source of iron and folic acid. ALOEVERA: It is okay as a topical gel, but aloe vera latex taken orally in powder or liquid form may cause low blood sugar, uterine contractions, or miscarriage. There's not enough information about safe doses in pregnancy, so it's probably best to avoid aloe vera juice and supplements. FENUGREEK: It is okay to use in normal quantities in cooking, but the larger quantities found in supplements may cause miscarriage or early labour.
GARLIC: When used in cooking, it is fine, but avoid large doses in supplements, as they may cause bleeding, miscarriage or early labour. GINGER: It is okay in cooking and in supplement doses of up to 100mg per day. Large doses can cause thinning of the blood and heartburn.
ALMOND OIL: Studies have found that using almond oil to prevent stretch marks was linked with increased risk of premature birth, while chamomile and liquorice may be linked to threatened miscarriage and premature birth.
To conclude, most foods are safe; however, eating some foods and drinks during pregnancy may increase the risk of harm to you and your baby and hence, best avoided.